A Comprehensive Overview of Three-Phase Separators: Internal Structure, Working Principles, Selection
Three-phase separators are vital components in the oil and gas industry, utilized for separating oil, gas, and water from well fluids. This article provides an in-depth examination of three-phase separators, delineating their internal structure, operational principles, and selection considerations.
Internal Structure of Three-Phase Separators:Three-phase separators typically come in two main configurations: horizontal and vertical separators. Horizontal separators feature a cylindrical vessel oriented horizontally, whereas vertical separators have a vertically oriented vessel. Both types of separators are equipped with internal components such as inlet diverters, baffles, mist extractors, and outlet weirs, designed to enhance phase separation.
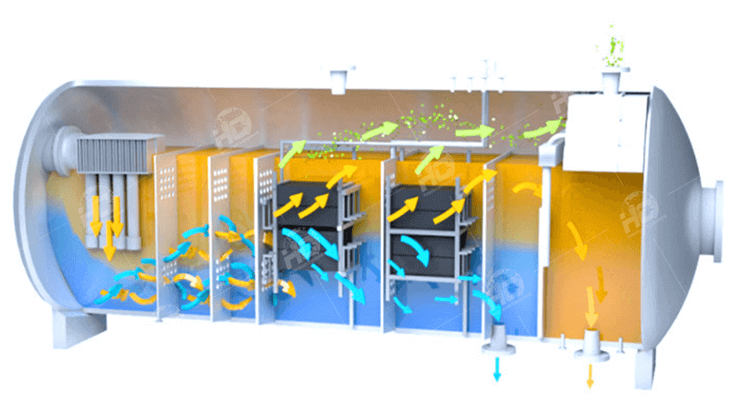
Working Principles of Three-Phase Separators:The operational principles of both horizontal and vertical separators involve the controlled introduction of well fluids into the vessel, where gravitational forces act to separate the oil, gas, and water phases. Gas rises to the top of the separator, while oil and water settle at different levels based on their densities. Internal components aid in this separation process by facilitating phase coalescence and preventing carryover.

Comparison between Horizontal and Vertical Separators:Horizontal separators are typically preferred for applications with high liquid-to-gas ratios, as they provide longer residence times and better separation efficiency for liquid droplets. They are also well-suited for low-pressure applications. On the other hand, vertical separators are preferred for applications with high gas-to-liquid ratios, as they offer better gas-liquid separation and are more space-efficient. Additionally, vertical separators are often used in high-pressure applications due to their compact design.
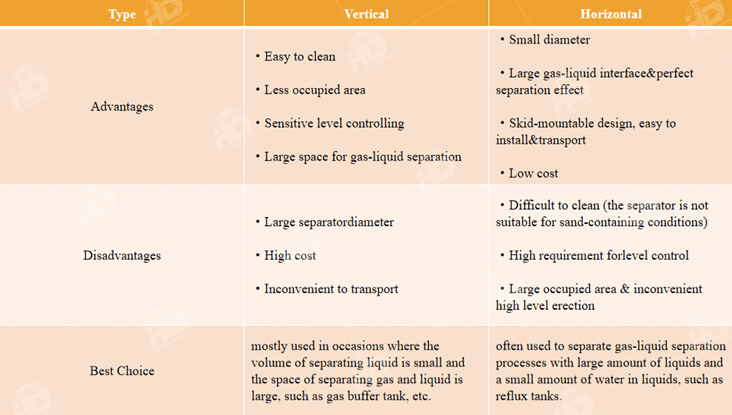
Selection of Three-Phase Separators:The selection of a three-phase separator depends on various factors, including fluid properties, flow rates, operating conditions, space constraints, and application requirements. Engineers must carefully consider these factors to choose the most suitable separator type and size for optimal performance and efficiency.
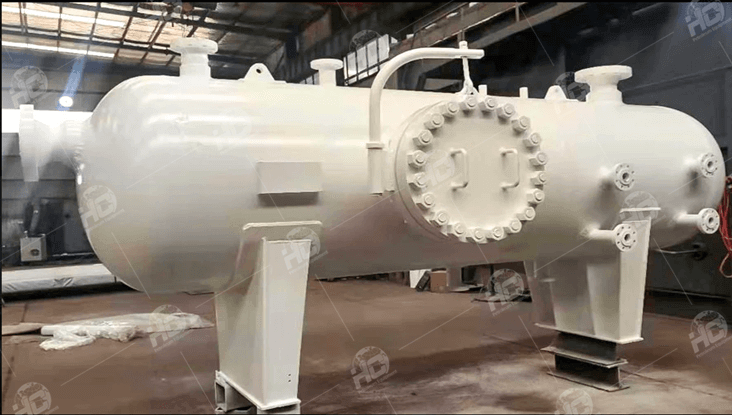

In summary, three-phase separators play a crucial role in the oil and gas industry, facilitating the separation of oil, gas, and water phases from well fluids. Understanding the differences between horizontal and vertical separators, as well as their internal structures, operational principles, and selection considerations, is essential for ensuring efficient production operations and maximizing hydrocarbon recovery.
