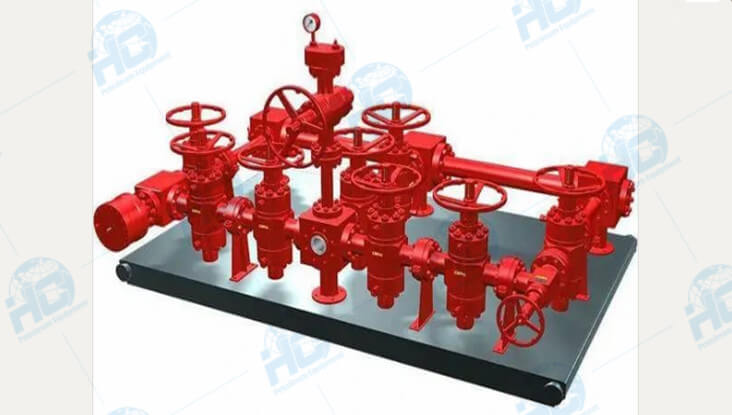
The Complexity of Operating a Well Testing Choke Manifold
In the realm of well testing, where precision and safety are paramount, the Well Testing Choke Manifold emerges as a pivotal tool for managing wellbore pressure and ensuring seamless operation. However, the operation of a Well Testing Choke Manifold is far from simple.
Operating a Well Testing Choke Manifold involves several intricate steps and considerations:
1. Precise Flow Regulation
Adjusting Chokes: The adjustable choke, the core component of the manifold, allows operators to fine-tune the flow rate and pressure. Selecting the correct choke size and adjusting it in real-time requires expertise to balance operational needs with safety requirements.
Dynamic Flow Management: Fluid flow rates can fluctuate due to reservoir conditions or operational changes, demanding constant monitoring and adjustment using the Well Testing Choke Manifold.
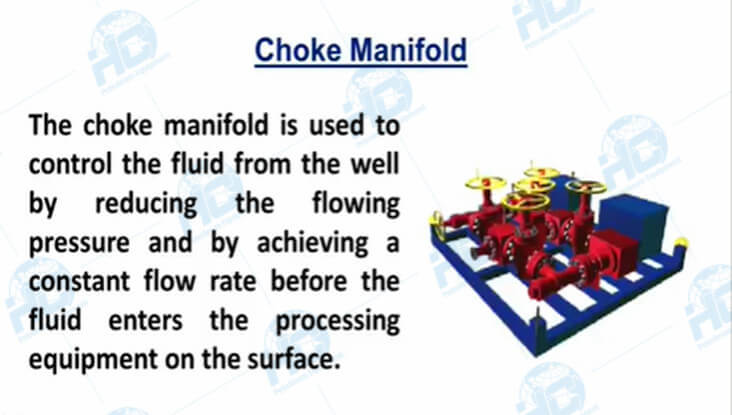
2. Pressure Control Across Multiple Stages
Pressure Surge Mitigation: Sudden pressure spikes in the wellbore can pose risks to both equipment and personnel. The Well Testing Choke Manifold’s ability to absorb and control these surges is critical, but it requires vigilant pressure monitoring and swift operational responses.
Safe Pressure Reduction: Reducing the wellhead pressure to levels suitable for downstream equipment, such as separators or pipelines, involves coordinated valve operation and continuous monitoring via the manifold.
3. Managing Multiphase Flow
Fluids exiting a well often comprise oil, gas, water, and solids, each with distinct flow characteristics. Ensuring consistent pressure control despite these variations adds to the operational complexity of the Well Testing Choke Manifold.
Operators must consider the potential for erosion, hydrate formation, or slug flow while configuring the manifold.

4. Coordination with Other Equipment
The Well Testing Choke Manifold operates in tandem with separators, heaters, and flow meters. Proper synchronization ensures that pressure control does not compromise the efficiency of the entire well testing system.
Operators must account for equipment limitations and adjust choke settings accordingly.
5. Emergency Response Readiness
In the event of an emergency, such as an unexpected blowout, the Well Testing Choke Manifold must be capable of immediately isolating the wellbore and shutting in the flow. This requires operators to be trained in emergency response protocols and familiar with the manifold's fail-safe mechanisms.
